Difference between revisions of "Atrazine"
(→Notes) |
Dronkers J (talk | contribs) |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{Tocright}} | |
{{Definition|title= atrazine | {{Definition|title= atrazine | ||
| − | |definition= Atrazine is an organic compound which is widely used as a herbicide. | + | |definition= Atrazine is an organic compound which is widely used as a herbicide. Atrazine is controversial due to its effects on nontarget species, such as on amphibians. Its use was banned from the European Union in 2004 but it remains one of the most widely used herbicides in the U.S.A.<ref name="Wiki">[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Atrazine www.wikipedia.org August 13 2009]</ref>. }} |
== Notes == | == Notes == | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | Atrazine was first used in the United States | + | Atrazine was first used in 1959 in the United States, where it currently still is one of the most widely used agricultural pesticides, with an annual production of over 35.000 tonnes. It is mainly used in sorghum, corn and sugarcane cultivation. It is released in the environment both from production sites as from its use as a herbicide. |
| + | <P> | ||
| + | Atrazine has a moderate water solubility of 30 mg/l, which makes it quite mobile in the environment. It is also [[persistent]] with a [[half-life]] in water of 150 days, and an even longer one in the soil. It has a relatively low tendency to [[adsorption|adsorb]] to soils or particles. Therefore, atrazine is expected to be present in surface water and groundwater. It has a low tendency to evaporate to the atmosphere and might afterwards be deposited by rainfall, although it is rapidly degraded in the atmosphere. | ||
| + | Atrazine has a very low tendency to [[bioaccumulation|bioaccumulate]] and is therefore not expected to [[biomagnification|biomagnify]] through [[food chain|food chains]]. | ||
| − | Atrazine has a moderate | + | Atrazine has a moderate [[toxic|toxicity]] in crustaceans and fish; acute lethal effects can induced by concentrations above 3mg/l, although some fish and crustacean species can tolerate atrazine concentrations above 80 mg/l. Phytoplankton is more vulnerable as toxic effects occur at concentrations of 60 µg/l. There have been reports that low concentrations of only 20 µg/l could change the behaviour of amphibians. Atrazine has also been suspected to induce [[endocrine disrupting compounds|endocrine disrupting effects]] in amphibians and mammals<ref name="Epa">[http://www.epa.gov/oppsrrd1/REDs/atrazine_combined_docs.pdf Interim Reregistration Eligibility Decision for Atrazine, U.S. EPA, January, 2003.]</ref>. |
| − | |||
| − | Atrazine has | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<P> | <P> | ||
<BR> | <BR> | ||
| Line 44: | Line 43: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| + | {{author | ||
| + | |AuthorID=19826 | ||
| + | |AuthorFullName=Daphnis De Pooter | ||
| + | |AuthorName=Daphnisd}} | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Toxicity chemicals]] |
Latest revision as of 13:02, 9 August 2020
Definition of atrazine:
Atrazine is an organic compound which is widely used as a herbicide. Atrazine is controversial due to its effects on nontarget species, such as on amphibians. Its use was banned from the European Union in 2004 but it remains one of the most widely used herbicides in the U.S.A.[1].
This is the common definition for atrazine, other definitions can be discussed in the article
|
Notes
| Atrazine |
|---|
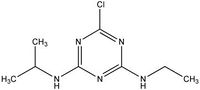
|
| Formula |
| C8H14ClN5 |
Atrazine was first used in 1959 in the United States, where it currently still is one of the most widely used agricultural pesticides, with an annual production of over 35.000 tonnes. It is mainly used in sorghum, corn and sugarcane cultivation. It is released in the environment both from production sites as from its use as a herbicide.
Atrazine has a moderate water solubility of 30 mg/l, which makes it quite mobile in the environment. It is also persistent with a half-life in water of 150 days, and an even longer one in the soil. It has a relatively low tendency to adsorb to soils or particles. Therefore, atrazine is expected to be present in surface water and groundwater. It has a low tendency to evaporate to the atmosphere and might afterwards be deposited by rainfall, although it is rapidly degraded in the atmosphere. Atrazine has a very low tendency to bioaccumulate and is therefore not expected to biomagnify through food chains. Atrazine has a moderate toxicity in crustaceans and fish; acute lethal effects can induced by concentrations above 3mg/l, although some fish and crustacean species can tolerate atrazine concentrations above 80 mg/l. Phytoplankton is more vulnerable as toxic effects occur at concentrations of 60 µg/l. There have been reports that low concentrations of only 20 µg/l could change the behaviour of amphibians. Atrazine has also been suspected to induce endocrine disrupting effects in amphibians and mammals[2].
Environmental standards and legislation
Included in the water framework list of priority substances
See also
References
Please note that others may also have edited the contents of this article.
|