Difference between revisions of "Measuring instruments for estuaries"
(→Instruments for estuaries) |
(→Instruments for estuaries) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
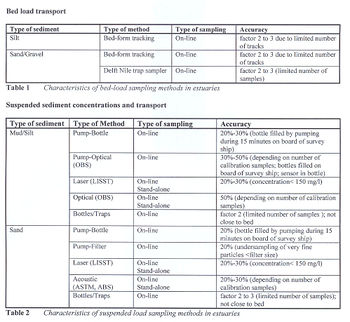
Table 1, 2 and 3 present the available instruments (and accuracies involved) for measuring: | Table 1, 2 and 3 present the available instruments (and accuracies involved) for measuring: | ||
* [[bed load]] transport, | * [[bed load]] transport, | ||
| − | * suspended sediment concentrations and transport rates | + | * [[suspended load|suspended]] sediment concentrations and transport rates |
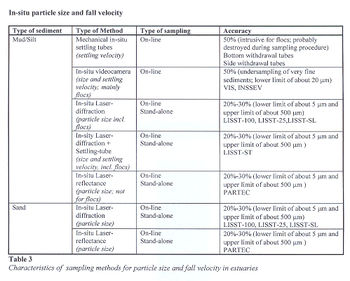
* particle sizes and fall velocities, | * particle sizes and fall velocities, | ||
| − | The order of preference is based on the overall sampling accuracy. Simple mechanical instruments such as the bottle-type and the trap-type samplers are not attractive because of the very short sampling times involved. Accuracy cannot be improved by increasing number of samples due to time-variation of sediment concentrations within the tidal cycle. | + | The order of preference in the Tables is based on the overall sampling accuracy. Simple mechanical instruments such as the bottle-type and the trap-type samplers are not attractive because of the very short sampling times involved. Accuracy cannot be improved by increasing number of samples due to time-variation of sediment concentrations within the tidal cycle. |
| − | Point-samples should be taken over the entire water column in strong tidal flows as the sediments will be mixed over the water column by turbulent eddies. Data sampling can be confined to the bottom region in weak tidal flows. Flocculation often is a dominant process in muddy estuaries. The LISST-ST which is an in-situ Laser diffraction instrument in combination with a settling tube offers a powerful solution to measure particle sizes, concentrations and densities of the individual particles as well as the flocculated aggregates (low concentrations <150 mg/l) in on-line mode. This instrument (LISST-ST) is not yet suitable for long-term, stand-alone measurements due to insufficient robustness, relatively low concentration range (<150 mg/l) and biological fouling problems. | + | Point-samples should be taken over the entire water column in strong tidal flows as the sediments will be mixed over the water column by turbulent eddies. Data sampling can be confined to the bottom region in weak tidal flows. Flocculation often is a dominant process in muddy estuaries. The LISST-ST which is an [[in-situ]] Laser diffraction instrument in combination with a settling tube offers a powerful solution to measure particle sizes, concentrations and densities of the individual particles as well as the flocculated aggregates (low concentrations <150 mg/l) in on-line mode. This instrument (LISST-ST) is not yet suitable for long-term, stand-alone measurements due to insufficient robustness, relatively low concentration range (<150 mg/l) and biological fouling problems (see also [[Optical Laser diffraction instruments (LISST)]]). |
[[Image:H533figure1.jpg|thumb|350px|left|Table 1 and 2: Instruments to measure bed load and suspended load]] | [[Image:H533figure1.jpg|thumb|350px|left|Table 1 and 2: Instruments to measure bed load and suspended load]] | ||
Revision as of 13:50, 4 December 2007
This article is a summary of sub-section 5.3.3 of the Manual Sediment Transport Measurements in Rivers, Estuaries and Coastal Seas[1]. This article describes which instruments are available to measure several aspects of sediment management in estuaries.
Contents
Instruments for estuaries
Table 1, 2 and 3 present the available instruments (and accuracies involved) for measuring:
- bed load transport,
- suspended sediment concentrations and transport rates
- particle sizes and fall velocities,
The order of preference in the Tables is based on the overall sampling accuracy. Simple mechanical instruments such as the bottle-type and the trap-type samplers are not attractive because of the very short sampling times involved. Accuracy cannot be improved by increasing number of samples due to time-variation of sediment concentrations within the tidal cycle.
Point-samples should be taken over the entire water column in strong tidal flows as the sediments will be mixed over the water column by turbulent eddies. Data sampling can be confined to the bottom region in weak tidal flows. Flocculation often is a dominant process in muddy estuaries. The LISST-ST which is an in-situ Laser diffraction instrument in combination with a settling tube offers a powerful solution to measure particle sizes, concentrations and densities of the individual particles as well as the flocculated aggregates (low concentrations <150 mg/l) in on-line mode. This instrument (LISST-ST) is not yet suitable for long-term, stand-alone measurements due to insufficient robustness, relatively low concentration range (<150 mg/l) and biological fouling problems (see also Optical Laser diffraction instruments (LISST)).
See also
Summaries of the manual
- Manual Sediment Transport Measurements in Rivers, Estuaries and Coastal Seas
- Chapter 1: Introduction, problems and approaches in sediment transport measurements
- Chapter 2: Definitions, processes and models in morphology
- Chapter 3: Principles, statistics and errors of measuring sediment transport
- Chapter 4: Computation of sediment transport and presentation of results
- Chapter 5: Measuring instruments for sediment transport
- Chapter 6: Measuring instruments for particle size and fall velocity
- Chapter 7: Measuring instruments for bed material sampling
- Chapter 8: Laboratory and in situ analysis of samples
- Chapter 9: In situ measurement of wet bulk density
- Chapter 10: Instruments for bed level detection
- Chapter 11: Argus video
- Chapter 12: Measuring instruments for fluid velocity, pressure and wave height
Other internal links
- Instrument characteristics of point-integrating suspended load samplers
- Guidelines for selection of sediment transport samplers
- Measuring instruments for rivers
- Measuring instruments for coasts
External links
- PDF of section 5.3 of the manual: [1]
References
- ↑ Rijn, L. C. van (1986). Manual sediment transport measurements. Delft, The Netherlands: Delft Hydraulics Laboratory
Please note that others may also have edited the contents of this article.
|
Please note that others may also have edited the contents of this article.
|