Difference between revisions of "Endosulfan"
(→Notes) |
(→Notes) |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
Endosulphan is moderately persistent in water. It's main metabolites is endosulphan sulphate which is more stable and equally toxic. In the soil endosulphan and endosulphan sulphate are highly persistent substances. It takes 120 days to half the concentration of endosulphan sulphate in the soil. | Endosulphan is moderately persistent in water. It's main metabolites is endosulphan sulphate which is more stable and equally toxic. In the soil endosulphan and endosulphan sulphate are highly persistent substances. It takes 120 days to half the concentration of endosulphan sulphate in the soil. | ||
Endosulphan is highly [[bioaccumulation|bioaccumulative]] and is expected to [[biomagnification|biomaginfy]]. | Endosulphan is highly [[bioaccumulation|bioaccumulative]] and is expected to [[biomagnification|biomaginfy]]. | ||
| − | At constant exposure | + | At constant exposure it is very toxic to all organisms. Concentrations below 1mg/l are toxic for all marine organisms, while concentrations of only 0,04 µg/l are already toxic for crustaceans. In rats doses above 18 mg per kg body weight can prove lethal. |
Endosulphan and endosulphan sulphate are potentially [[endocrine disrupting compounds]]: in vivo tests with fish show that endosulphan induces changes on ovaries, developmental changes and has an impact on their behavior. | Endosulphan and endosulphan sulphate are potentially [[endocrine disrupting compounds]]: in vivo tests with fish show that endosulphan induces changes on ovaries, developmental changes and has an impact on their behavior. | ||
Revision as of 13:36, 5 August 2009
Definition of endosulphan:
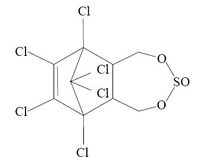
Endosulphan is a synthetic pesticide which belongs to the group of organochlorine compounds with a sulfite group. [1]
This is the common definition for endosulphan, other definitions can be discussed in the article
|
Notes
| Endosulphan |
|---|
|
| Formula |
| C9H6Cl6O3S |
Endosulphan is used as a insecticide on a wide variety of insects and mites, predominantly in temperate, subtropic and tropic climatic zones. In Europe it has been used for more than 40 years. Currently it is used at 340 tonnes per year, mainly in Spain but also in Belgium, France, Portugal and Switzerland. Endosuphan enters rivers by run-of from treated areas. The rivers transport it to the sea. It can also enter the ocean though atmospheric transport. [1]
Endosulphan is moderately persistent in water. It's main metabolites is endosulphan sulphate which is more stable and equally toxic. In the soil endosulphan and endosulphan sulphate are highly persistent substances. It takes 120 days to half the concentration of endosulphan sulphate in the soil. Endosulphan is highly bioaccumulative and is expected to biomaginfy. At constant exposure it is very toxic to all organisms. Concentrations below 1mg/l are toxic for all marine organisms, while concentrations of only 0,04 µg/l are already toxic for crustaceans. In rats doses above 18 mg per kg body weight can prove lethal. Endosulphan and endosulphan sulphate are potentially endocrine disrupting compounds: in vivo tests with fish show that endosulphan induces changes on ovaries, developmental changes and has an impact on their behavior.
Endosulphan concentrations of 0,06 μg/l have been found in water and of 81,6 μg/kg in the sediment. These are concentrations which can cause harm to organisms.[1]
Environmental standards and legislation
Included in the OSPAR list of substances of priority action
Included in the water framework list of priority substances
See also
OSPAR background document on endosulphan