Difference between revisions of "Danube Delta"
Dronkers J (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (16 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
<u>'''Main coastal issues'''</u> | <u>'''Main coastal issues'''</u> | ||
| − | + | *Habitat (anthropic and natural) degradation | |
| − | + | *Loss of biodiversity | |
| − | + | *Global Changes impacts on population livelihood and wellbeing | |
| − | + | *Coastal/Sea Spatial Planning | |
| − | <u>'''Relation between the | + | <u>'''Relation between the coastal issues and the ICZM protocol principles and articles'''</u> |
| − | + | The tendency of overexploitation of the natural resources, that brought about important changes in the delta subsystems, has caused the derangement of the natural equilibrium: the disappearance of some zones of fish natural reproduction and of other animal species, the clogging of natural streams and characteristic landscapes, the cutting of some oversized channels. | |
| − | + | Negative effects generated by the human activity inside the delta, as well as those much more intensely generated in the hydrographic basin have influenced the balance of the natural ecosystems. Therefore, it is necessary to take measures for reducing those effects, recovering the affected zones and protecting the existent ones with special value. | |
| + | |||
| + | The above-presented situation was an important reason for declaring the Danube Delta a biosphere reserve, which should fulfil the following conditions: | ||
| − | + | *It must preserve characteristic ecosystems by strictly protected areas without excluding the traditional use of the fish and reed resources; | |
| − | + | *It must be a zone for monitoring, research, education and instruction regarding the environment protection; | |
| − | + | *It must be a place where government and regional decision people, scientists and local people co-operate in order to achieve an administration model, so that they should meet the human necessities, in accordance with the preservation of the biological resources and natural ecosystems. | |
| − | + | {| border="1" cellspacing="0" width="600px" style="margin: 1em auto 1em auto;" | |
| + | |+ <span style="Font-size: 120%">'''Table 1: Sinergies between ICZM Protocol, Biosphere Reserve Law of Danube Delta and Romanian National ICZM Law.'''</span> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| − | + | ! width="10%" |Nr. | |
| + | ! [http://www.pap-thecoastcentre.org/razno/PROTOCOL%20ENG%20IN%20FINAL%20FORMAT.pdf ICZM] | ||
| + | ! [http://www.ddbra.ro/informatii-publice/legisla-ie/legislatia-privind-activitatea-administratiei-rezervatiei-biosferei-delta-dunarii-a791 DD Biosphere Reserve Law (82/1993)] | ||
| + | ! [http://www.lege-online.ro/lr-LEGE-280-2003-(44664).html National ICZM Law (280/2003)] | ||
| − | Black Sea as a big hydrographic basin and unique ecosystem is extremely sensitive exposed to serious threats as pollution, habitats degradation, biodiversity decline, overexploitation of resources, coastal erosion, etc. Thus, within this activity were identified main regional indicators: physic-chemical indicators, indicators for marine living resources and general coastal zone impact indicators (population, land use, agriculture, tourism, coastal erosion). | + | |- |
| + | |||
| + | | 1. | ||
| + | | 3. Geographical coverage | ||
| + | |1./2. | ||
| + | |2. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |||
| + | | 2. | ||
| + | | 8. Protection and sustainable use | ||
| + | |3./6. | ||
| + | |5/12 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |||
| + | |3. | ||
| + | |9. Economic activities | ||
| + | |6. | ||
| + | |7/8/14/18-30 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |||
| + | |4. | ||
| + | |10. Specific ecosystems | ||
| + | |6. | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |||
| + | |5. | ||
| + | |13. Cultural heritage | ||
| + | |||
| + | |6./8. | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |6. | ||
| + | |15. Awarness-raising, training education and research | ||
| + | |6. | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |7. | ||
| + | |16. Monitoring | ||
| + | |6. | ||
| + | |10. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |8. | ||
| + | |19. Environment assessment | ||
| + | |6. | ||
| + | |39-50 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |9. | ||
| + | |20. Land policy | ||
| + | |6. | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |10. | ||
| + | |21. Economical, financial and fiscal instruments | ||
| + | |7. | ||
| + | |61. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |11. | ||
| + | |30. Focal points | ||
| + | |4. | ||
| + | |68. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 12. | ||
| + | |2. Definitions CZ | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |Annex 1 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |13. | ||
| + | |4. Preservation rights | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |1. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |14. | ||
| + | |5. Objectives ICZM | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |2. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |15. | ||
| + | |6. General Principles | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |5. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |16. | ||
| + | |11. Coastal Landscape | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |17. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |17. | ||
| + | |14. Participation | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |69-72 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |18. | ||
| + | |18. National Coastal Strategies, Plans and Programs | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |All | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |19. | ||
| + | |32. Institutional Coordination | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |83-87 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <u>'''Relevance of the coastal issues'''</u> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Black Sea as a big hydrographic basin and unique ecosystem is extremely sensitive and exposed to serious threats as pollution, habitats degradation, biodiversity decline, overexploitation of resources, coastal erosion, etc. Thus, within this activity were identified main regional indicators: physic-chemical indicators, indicators for marine living resources and general coastal zone impact indicators (population, land use, agriculture, tourism, coastal erosion). | ||
| Line 52: | Line 186: | ||
- Regulation of economical activities on ecological bases | - Regulation of economical activities on ecological bases | ||
| − | - Protection and rehabilitation of habitats and ecosystems | + | - Protection and [[Ecosystem rehabilitation|rehabilitation]] of habitats and ecosystems |
<br style="clear:both;"/> | <br style="clear:both;"/> | ||
| Line 72: | Line 206: | ||
<u>'''PEGASO tools developed and used'''</u> | <u>'''PEGASO tools developed and used'''</u> | ||
| − | Indicators - LEAC - Scenarios - Participatory methods. | + | Indicators - LEAC - Scenarios - [[Participation in the Danube delta|Participatory methods]]. |
| Line 78: | Line 212: | ||
SketchMetch method (Spatial planning tool) | SketchMetch method (Spatial planning tool) | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| Line 91: | Line 220: | ||
<span style="color: Blue"><small>Elaboration: Stefano Soriani, Fabrizia Buono, Monica Camuffo, Marco Tonino, University Ca’ Foscari of Venice.</small></span> | <span style="color: Blue"><small>Elaboration: Stefano Soriani, Fabrizia Buono, Monica Camuffo, Marco Tonino, University Ca’ Foscari of Venice.</small></span> | ||
| + | [[Category:PEGASO study sites]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:24, 8 October 2021
CASE description
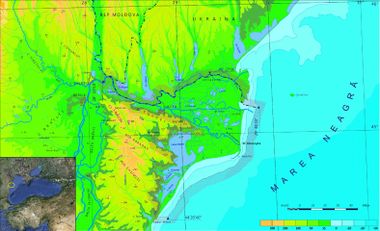
The coast of Danube Delta (Romania) comprised between Musura branch and Midia cape in South (166 km) is characterized by sandy beaches and low altitudes less steep underwater slopes.
ICZM phase
Main coastal issues
- Habitat (anthropic and natural) degradation
- Loss of biodiversity
- Global Changes impacts on population livelihood and wellbeing
- Coastal/Sea Spatial Planning
Relation between the coastal issues and the ICZM protocol principles and articles
The tendency of overexploitation of the natural resources, that brought about important changes in the delta subsystems, has caused the derangement of the natural equilibrium: the disappearance of some zones of fish natural reproduction and of other animal species, the clogging of natural streams and characteristic landscapes, the cutting of some oversized channels.
Negative effects generated by the human activity inside the delta, as well as those much more intensely generated in the hydrographic basin have influenced the balance of the natural ecosystems. Therefore, it is necessary to take measures for reducing those effects, recovering the affected zones and protecting the existent ones with special value.
The above-presented situation was an important reason for declaring the Danube Delta a biosphere reserve, which should fulfil the following conditions:
- It must preserve characteristic ecosystems by strictly protected areas without excluding the traditional use of the fish and reed resources;
- It must be a zone for monitoring, research, education and instruction regarding the environment protection;
- It must be a place where government and regional decision people, scientists and local people co-operate in order to achieve an administration model, so that they should meet the human necessities, in accordance with the preservation of the biological resources and natural ecosystems.
| Nr. | ICZM | DD Biosphere Reserve Law (82/1993) | National ICZM Law (280/2003) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 3. Geographical coverage | 1./2. | 2. |
| 2. | 8. Protection and sustainable use | 3./6. | 5/12 |
| 3. | 9. Economic activities | 6. | 7/8/14/18-30 |
| 4. | 10. Specific ecosystems | 6. | |
| 5. | 13. Cultural heritage | 6./8. | |
| 6. | 15. Awarness-raising, training education and research | 6. | |
| 7. | 16. Monitoring | 6. | 10. |
| 8. | 19. Environment assessment | 6. | 39-50 |
| 9. | 20. Land policy | 6. | |
| 10. | 21. Economical, financial and fiscal instruments | 7. | 61. |
| 11. | 30. Focal points | 4. | 68. |
| 12. | 2. Definitions CZ | Annex 1 | |
| 13. | 4. Preservation rights | 1. | |
| 14. | 5. Objectives ICZM | 2. | |
| 15. | 6. General Principles | 5. | |
| 16. | 11. Coastal Landscape | 17. | |
| 17. | 14. Participation | 69-72 | |
| 18. | 18. National Coastal Strategies, Plans and Programs | All | |
| 19. | 32. Institutional Coordination | 83-87 |
Relevance of the coastal issues
Black Sea as a big hydrographic basin and unique ecosystem is extremely sensitive and exposed to serious threats as pollution, habitats degradation, biodiversity decline, overexploitation of resources, coastal erosion, etc. Thus, within this activity were identified main regional indicators: physic-chemical indicators, indicators for marine living resources and general coastal zone impact indicators (population, land use, agriculture, tourism, coastal erosion).
Objectives
- Improvement of coastal ecosystem knowledge
- Biodiversity conservation
- Regulation of economical activities on ecological bases
- Protection and rehabilitation of habitats and ecosystems
End Products
- Creation of a database for ICZM
- Development of thematic maps
- Organisational design in the field of maritime spatial planning
- Elaboration of a preliminary ICZM strategy
- Project proposal for new funding
PEGASO tools developed and used
Indicators - LEAC - Scenarios - Participatory methods.
Other tools to be applied
SketchMetch method (Spatial planning tool)
CASE Responsible
Iulian Nichersu - Danube Delta national Institute for Research and Development, Tulcea - email: iuli@indd.tim.ro
Elaboration: Stefano Soriani, Fabrizia Buono, Monica Camuffo, Marco Tonino, University Ca’ Foscari of Venice.