Difference between revisions of "Chlorfenvinphos"
(ref +ref) |
(→See also) |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
[http://www.vliz.be/projects/endis/EDnorth.php?showchemprop=true&showeffects=true&chemeffects=true&chemid=152 Benzene on the ED North Database] | [http://www.vliz.be/projects/endis/EDnorth.php?showchemprop=true&showeffects=true&chemeffects=true&chemid=152 Benzene on the ED North Database] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<P> | <P> | ||
<BR> | <BR> | ||
Revision as of 14:35, 13 August 2009
Definition of Chlorfenvinphos:
Chlorfenvinphos is the common name of an insecticide used to control insect pests on livestock. It was also used to control household pests such as flies, fleas, and mites. The pure chemical is a colourless liquid with a mild odour. [1]
This is the common definition for Chlorfenvinphos, other definitions can be discussed in the article
|
Notes
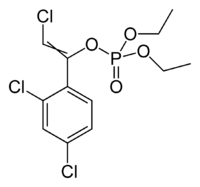
| Chlorfenvinphos |
|---|
|
| Formula |
| C12H14Cl3O4P |
Chlorfenvinphos was introduced in the US in 1963 where it was used until 1991. No information is available about the volumes in which it was used.
Chlorfenvinphos enters the environment from run-off after rainfall and leaching from hazardous waste sites. After it has leached, it may be present in the soil and underground water. It has a water solubility of 130mg/l and therefore may be present in surface water after it has run off the land. It has a moderate tendency to adsorb to particles. In water is very stable although some biodegradation might occur by micro-organisms.
It may have a low to moderate tendency to bioaccumulate, however no experimental data on fishes are available. There is also no information available on whether it biomagnifies.[1]
It is very toxic for fishes, some species die at concentrations above 25 µg/l, although some can tolerate concentrations up to 1 mg/l. Zooplankton are even more vulnerable, some species die at concentrations above 0.4 µg/l. [2] No information is available now to show that it can be found in marine wildlife.
Environmental standards and legislation
Included in the water framework list of priority substances
See also
Benzene on the ED North Database