Difference between revisions of "Black Sea"
Dronkers J (talk | contribs) |
Dronkers J (talk | contribs) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | |||
== Local environment == | == Local environment == | ||
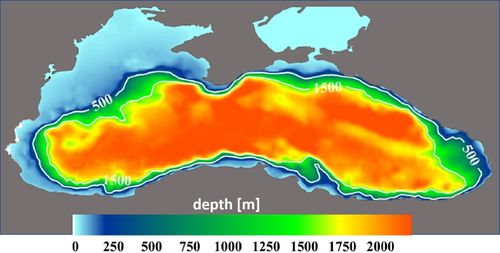
| − | The Black Sea is a unique marine environment. It is an enclosed coastal basin with | + | The Black Sea is a unique marine environment. It is an enclosed coastal basin with a small [[Estuarine circulation|density-driven echange flow]] with the Mediterranean. The maximum depth in the central part of the Black Sea exceeds 2000 m; the connection with the Mediterranean (the Bosporus) has a sill located at −36.5 m. Below the [[halocline]] at about 200 m, the water is permanently devoid of oxygen; about 87% of the Black Sea water mass is anoxic and contains high levels of hydrogen sulphide. The Black Sea houses a wide variety of [[habitat]] types but has a relatively low diversity of species compared to the Mediterranean. Historically, the Black Sea was one of the most biologically productive regions in the world. |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:BlackSeaBathymetry.jpg|thumb|500px|center|Black Sea bathymetry]] | ||
| + | |||
== Specific biodiversity issues == | == Specific biodiversity issues == | ||
| − | Among the coastal basins of the world's oceans, the environmental degradation in the Black Sea is thought to be the most severe. Threats to Black Sea [[biodiversity]] are the introduction of alien species, commercial fisheries and overexploitation of resources, chemical contamination, especially from oil products, [[eutrophication]] (nutrient enrichment from plant matter) and [[pollution]] from agriculture, industry and sewage. | + | Among the coastal basins of the world's oceans, the environmental degradation in the Black Sea is thought to be the most severe. Threats to Black Sea [[biodiversity]] are the [[Non-native species invasions|introduction of alien species]], commercial fisheries and [[overexploitation]] of resources, chemical contamination, especially from [[Coastal pollution and impacts#Oil and gas and offshore installations|oil products]], [[Possible consequences of eutrophication|eutrophication]] (nutrient enrichment from plant matter) and [[Coastal pollution and impacts|pollution]] from agriculture, industry and sewage. |
| + | |||
| + | Most non-native species in the Black Sea have been introduced in [[ballast water]]s from shipping. Low species diversity combined with high habitat diversity in the region provides favourable conditions for invasive species, which can disrupt the stability and functioning of ecosystems and represents the biggest threat to [[biodiversity]] in the Black Sea. Critically low oxygen levels also occur in the upper layer of the Black Sea, mainly due to high nutrient input from the rivers. This has led to dramatic reduction in fish catches. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Detailed information about the Black Sea can be found on the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Black_Sea Wikipedia]. | ||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ==Related articles== |
*[[Black Sea Convention]] | *[[Black Sea Convention]] | ||
*[[Marine Biotechnology in Black Sea basin]] | *[[Marine Biotechnology in Black Sea basin]] | ||
*[[Enabling a shared information infrastructure for Mediterranean and Black Sea basins]] | *[[Enabling a shared information infrastructure for Mediterranean and Black Sea basins]] | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | See also: | |
| − | + | :[http://www.blacksea-commission.org/_environment.asp Commission on the Protection of the Black Sea Against Pollution] | |
[[Category:Black sea]] | [[Category:Black sea]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:24, 10 March 2021
Local environment
The Black Sea is a unique marine environment. It is an enclosed coastal basin with a small density-driven echange flow with the Mediterranean. The maximum depth in the central part of the Black Sea exceeds 2000 m; the connection with the Mediterranean (the Bosporus) has a sill located at −36.5 m. Below the halocline at about 200 m, the water is permanently devoid of oxygen; about 87% of the Black Sea water mass is anoxic and contains high levels of hydrogen sulphide. The Black Sea houses a wide variety of habitat types but has a relatively low diversity of species compared to the Mediterranean. Historically, the Black Sea was one of the most biologically productive regions in the world.
Specific biodiversity issues
Among the coastal basins of the world's oceans, the environmental degradation in the Black Sea is thought to be the most severe. Threats to Black Sea biodiversity are the introduction of alien species, commercial fisheries and overexploitation of resources, chemical contamination, especially from oil products, eutrophication (nutrient enrichment from plant matter) and pollution from agriculture, industry and sewage.
Most non-native species in the Black Sea have been introduced in ballast waters from shipping. Low species diversity combined with high habitat diversity in the region provides favourable conditions for invasive species, which can disrupt the stability and functioning of ecosystems and represents the biggest threat to biodiversity in the Black Sea. Critically low oxygen levels also occur in the upper layer of the Black Sea, mainly due to high nutrient input from the rivers. This has led to dramatic reduction in fish catches.
Detailed information about the Black Sea can be found on the Wikipedia.
Related articles
- Black Sea Convention
- Marine Biotechnology in Black Sea basin
- Enabling a shared information infrastructure for Mediterranean and Black Sea basins
See also: