Difference between revisions of "Mecoprop"
Dronkers J (talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| + | |||
{{author | {{author | ||
|AuthorID=19826 | |AuthorID=19826 | ||
|AuthorFullName=Daphnis De Pooter | |AuthorFullName=Daphnis De Pooter | ||
|AuthorName=Daphnisd}} | |AuthorName=Daphnisd}} | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | |
| + | [[Category:Toxicity chemicals]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:24, 9 August 2020
Notes
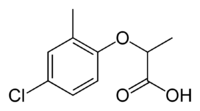
| Mecoprop |
|---|
|
| Formula |
| C10H11ClO3 |
MCPP is mainly used to control weeds around cereal crops, apples and pears. The release of mecoprop to the environment will be primarily from its application as a herbicide, but also potentially from its manufacture, transport and storage. There are no natural sources[1].
In water it has a low solubility of 0,734 g/l. It has a low tendency to adsorb to organic matter and soils and has a half-life in water of less than a month[3].
MCPP has a low potential to bioaccumulate and is therefore not likely to biomagnify[3].
Mecoprop causes acute toxicity in oysters at concentrations above 4 mg/l. Most fish species survive short exposure to concentrations of 10 mg/l and some survive short exposure to concentrations up to 500 mg/l[4].
Environmental standards and legislation
Included in the water framework list of priority substances
References
Please note that others may also have edited the contents of this article.
|