Difference between revisions of "Overtopping resistant dikes"
Dronkers J (talk | contribs) |
Dronkers J (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| − | In 1953 the Netherlands experienced a major flooding. Studies determined that | + | In 1953 the Netherlands experienced a major flooding. Studies determined that most of the dike breaches were caused by overtopping (and even overflowing) of the dikes; failure started at the landward slope of the structures<ref>Gerritsen, H. 2005. What happened in 1953? The Big Flood in the Netherlands in retrospect. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 363: 1271–1291</ref>. At that time, all dikes had a rather low crest and were built with a steep landward slope. Since then all major water defences were raised and the landward slopes were made more gentle. The dikes in the western part of the Netherlands were raised such that overtopping rates exceeding 0.1 l/s per meter would have a probability not greater than 1/10,000 per year. In the 1990ties it was decided by law that all major water defences should be periodically assessed for safety (periodicity of about 6 years). In the first safety assessment it was found that a large number of dikes had to be raised again in order to comply with the safety standards. This raised the question if the method to determine the rate of wave overtopping was correct or not. Also the question was put forward if the safety standard of 0.1 l/s per meter with a 1/10,000 probability was adequate. It turned out that the flooding mechanisms were not understood well enough and that the safety standard was wrongfully determined on basis of testing with overflow instead of overtopping. Additionally, failure mechanisms were not adequately described. This lead to a Dutch national research program on loads on and strength of flood defences. To assess the erosion strength of grass covers on inner slopes and transition zones between slope to horizontal flats, destructive tests using a Wave Overtopping Simulator were performed at several dikes in the Netherlands. A Wave Overtopping Simulator (see Fig. 3) performs destructive tests on inner slopes of real dikes in order to establish the erosion resistance against overtopping waves from severe storms. |
| − | |||
| − | A Wave Overtopping Simulator performs destructive tests on inner slopes of real dikes in order to establish the erosion resistance against overtopping waves from severe storms. | ||
| − | |||
==Definition, design and function== | ==Definition, design and function== | ||
| − | Dikes and levees are applied | + | Dikes and levees are applied wherever a hinterland needs protection against flooding. These protection measures prevent an area from flooding thus enabling economic and social activities also at high water levels. The dikes are designed in such a way that they are geotechnically stable under normal and extreme conditions. Dutch dikes are designed to avoid overtopping. Of course no overtopping cannot be guaranteed. The structures which are described here are mainly dikes with grass-covered inner (landward) slopes such as the ones found in the Netherlands. They are mostly made with a sand core covered by a clay layer on the slopes and the crest. |
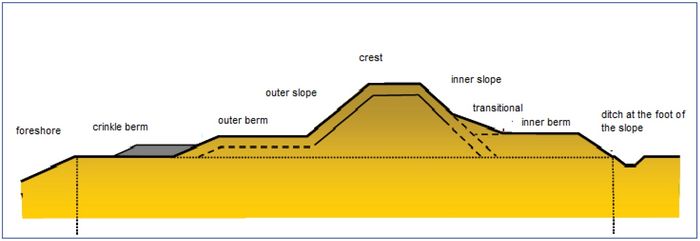
[[Image:DutchSeadike.jpg|thumb|center|700px|Figure 1: Cross section of a Dutch seadike]] | [[Image:DutchSeadike.jpg|thumb|center|700px|Figure 1: Cross section of a Dutch seadike]] | ||
| − | The typical geometry of dikes and levees is an outer or seaward slope then a crest and then a landward slope (right-hand side of Figure 1). The function of the landward slopes is stability of the dike structure and | + | The typical geometry of dikes and levees is an outer or seaward slope then a crest and then a landward slope (right-hand side of Figure 1). The function of the landward slopes is to ensure stability of the dike structure and to guide overtopping waves or water flowing over the crest to the inlands. The landward slopes must be able to resist loads induced by design conditions. The slope angles as well as the width of the crest vary. In the Dutch case, sea dikes have a typical landward slope 1v:3h. River dikes are mostly steeper, up to 1v:2h. The height of the dikes is also highly variable. It depends on the local hydraulic conditions and on the norm frequency of water level for which the dike is designed. This varies from 1/10,000 per year for sea defences in the western part of the Netherlands to 1:1,250 years for dikes along rivers. |
| − | Dikes and levees protect up to a certain level. Absolute safety is impossible. The level to which a dike or a levee protects from flooding depends on the hydraulic regime, the physics of the structure (geometric and geotechnical) and the intended risk reduction or allowable risk to which it is designed. This implies that an economic optimum or in | + | Dikes and levees protect up to a certain level. Absolute safety is impossible. The level to which a dike or a levee protects from flooding depends on the hydraulic regime, the physics of the structure (geometric and geotechnical) and the intended risk reduction or allowable risk to which it is designed. This implies that an economic optimum (or in some cases the availability of funds) defines the achievable level of risk reduction. More than half of the Netherlands is below sea level and therefore has to be protected by dikes or other flood protection structures (including dunes). The dikes in the Netherlands are currently designed based on exceedance of a certain water level that is extrapolated from a long time series (over 200 years) and scientific hindcasting. From these water levels, corresponding wave action is calculated. The combination of water level and hydraulic conditions determines the design conditions. Back in 1956, the first Delta Committee already did some early calculations and concluded that the level of protection of the western part of the Netherlands should be higher than in other parts (highest economic value). They found that this part should have a protection level (based on exceedance of water level) of 1/100,000 per year. They knew dikes to have a large residual strength in the designs. They assumed this to be a factor 10 resulting in lowering the norm to once in ten thousand years. In 1996 the safety levels in the Netherlands were registered in the Water Defence Act. In 2009 this Act was replaced by the Water Act. In the Act of 1996 it was stated that the basis for the safety standards should be transformed from exceedance of a certain water level to a risk based approach. |
==Experimental experience with function and performance== | ==Experimental experience with function and performance== | ||
===Onset=== | ===Onset=== | ||
| − | The landward slope of dikes proved a weak spot during the flooding of 1953 in the Netherlands (over 1,800 people drowned). Back then the dikes were much lower than today. This event led to the Delta Plan recommended heightening the dikes and to | + | The landward slope of dikes proved a weak spot during the flooding of 1953 in the Netherlands (over 1,800 people drowned). Back then the dikes were much lower than today. This event led to the Delta Plan recommended heightening the dikes and to reduce the landward slopes to 1:3 or even milder to mitigate the erosive impact of overtopping waves. Before 1953 the landward slopes were very steep, 1:2 or even steeper. Another example is the impact of hurricane Katrina on New Orleans where many landward slopes failed before the water level reached the crest of the levees. Water coming over the dikes or levees does not necessarily mean danger. If the area can cope with a certain amount of water without causing any or just minor socio-economic damage, it may be allowable. To optimize costs and competition for space, the dimensions needed for flood protection is preferably limited. Allowing some water passing the crest of the dike by overtopping waves implies that the need to heighten (and widen) the dikes decreases. If the dikes are strong enough and the amount of overtopping water can be handled, the design level of the structure can be lowered. However, the effect of overtopping water passing the crest of dikes was not well known. |
[[Image:WaveOvertoppingSimulator.jpg|thumb|left|400px|Figure 2: Principle of the Wave Overtopping Simulator. From Van der Meer 2008<ref name="VDM08"/>.]] | [[Image:WaveOvertoppingSimulator.jpg|thumb|left|400px|Figure 2: Principle of the Wave Overtopping Simulator. From Van der Meer 2008<ref name="VDM08"/>.]] | ||
| Line 28: | Line 25: | ||
===Test results=== | ===Test results=== | ||
| − | [[Image:WaveOvertoppingExperiment.jpg|thumb|left|250px|Figure | + | [[Image:WaveOvertoppingExperiment.jpg|thumb|left|250px|Figure 1: Release of a wave from the simulator. From Van der Meer 2008<ref name="VDM08"/>.]] |
| − | The process of wave overtopping on | + | The process of wave overtopping on dikes and levees is fairly well known (Overtopping Manual, 2018<ref name=OM>[http://www.overtopping-manual.com/ Van der Meer, J.W., Allsop, N.W.H., Bruce, T., De Rouck, J., Kortenhaus, A., Pullen, T., Schüttrumpf, H., Troch, P. and Zanuttigh, B. 2018. EurOtop manual]</ref>). In contrast, the erosive impact of wave overtopping is not well known, mainly due to the fact that research on this topic cannot be performed on a small scale, as it is practically impossible to scale clay and grass down properly. Only some tests have been performed in large wave flumes, like the Delta flume in the Netherlands and the GWK in Germany, see Smith (1994<ref>Smith, G.M., 1994. Grasdijken. Graserosie, reststerkte en golfoverslag. WL|Delft Hydraulics report H1565 (In Dutch)</ref>) and Oumeraci et al. (2000<ref>Oumeraci, H., Schüttrumpf, H., Möller, J., and Kudella, M., 2000. Large scale model tests on wave overtopping with natural sea states. LWI-Bericht Nr. 852.</ref>). Therefore, the Wave Overtopping Simulator has been developed; see Van der Meer et al. (2006<ref name="VDM06">Van der Meer, J.W., Bernardini, P, Akkerman, G.J., and Hoffmans, G.J.C.M., 2007. The wave overtopping simulator in action. ASCE, proc Coastal Structures, Venice, Italy. Van der Meer, J.W., W. Snijders and E. Regeling, 2006. The wave overtopping simulator. ASCE, proc. ICCE 2006, San Diego, 4654-4666.</ref>, 2007<ref name="VDM07">Van der Meer, J.W., Steendam, G.J., de Raat, G. and Bernardini, P., 2008. Further developments on the wave overtopping simulator. ASCE, proc. ICCE 2008, Hamburg. Van der Meer, J.W., 2007. Design, construction, calibration and use of the wave overtopping simulator. ComCoast, Workpackage 3: Development of Alternative Overtopping-Resistant Sea Defences, phase 3. [www.comcoast.org].</ref> and 2008<ref name="VDM08">Van der Meer, J.W., 2008. Erosion strength of inner slopes of dikes against wave overtopping. Preliminary conclusions after two years of testing with the Wave Overtopping Simulator. Summary Report.</ref>) for more details. The Simulator consists of a high-level mobile box to store water. The maximum capacity is 5.5 m<sup>3</sup> per m width (22 m<sup>3</sup> for a 4 m wide Simulator). This box is continuously filled with a predefined discharge and emptied at specific times in such a way that it simulates the overtopping tongue of a wave at the crest and inner slope of a dike, see Fig. 3. The discharge of water is released in such a way that for each overtopping volume of water the flow velocity and thickness of the water tongue at the crest corresponds with the characteristics that can be expected. |
[[Image:WaveOvertoppingVolume.jpg|thumb|right|400px|Figure 4: Distribution of overtopping volumes of waves for sea dikes and various mean overtopping discharges, as simulated by the Wave Overtopping Simulator, based on Hs = 2 m and wave steepness 0.04 (peak period). From Van der Meer 2008<ref name="VDM08"/>.]] | [[Image:WaveOvertoppingVolume.jpg|thumb|right|400px|Figure 4: Distribution of overtopping volumes of waves for sea dikes and various mean overtopping discharges, as simulated by the Wave Overtopping Simulator, based on Hs = 2 m and wave steepness 0.04 (peak period). From Van der Meer 2008<ref name="VDM08"/>.]] | ||
| Line 41: | Line 38: | ||
[[Image:WaveOvertoppingDamage1.jpg|thumb|right|400px|Figure 5: Example of damage by the wave overtopping simulation. From Van der Meer 2008<ref name="VDM08"/>.]] | [[Image:WaveOvertoppingDamage1.jpg|thumb|right|400px|Figure 5: Example of damage by the wave overtopping simulation. From Van der Meer 2008<ref name="VDM08"/>.]] | ||
| + | |||
Inner slopes of a dike, covered with grass on clay, never failed by overtopping wave erosion for a mean overtopping discharge of 30 l/s per m or less. Only one section failed at 50 l/s per m; some although not all at 75 l/s per m (example Fig. 5). Large erosion resistance of the inner slope of a dike is determined by the combination of grass and clay. The grass cover seems stronger if it grows on sandy clay and may even resist up to 75 l/s per m. But if significant damage occurs, the clay layer is not very erosion resistant. Since grass roots can barely penetrate good quality clay, no strong grass cover could be found. Here grass may rip off for overtopping discharges around 30 l/s per m although the remaining good quality clay layer, still reinforced with some roots, has a large erosion resistance against overtopping waves. Therefore a good grass cover on a sandy clay and a worse grass cover on good clay show different failure mechanisms but similar strength against wave overtopping. Thus the grass sod and its way of maintenance may have less influence on the total strength than previously anticipated. Bad grass coverage (small open areas without grass) on sandy clay may show less resistance. Transitions from slope to horizontal such as the transition from the inner slope to the toe of the dike are probably the most critical locations for initial and increasing damage. Damage here was initiated by a mean discharge of 10 l/s per m or more. As the damage occurred at the lowest part of the inner slope it will take time for damage to extend to the crest level and subsequently cause a dike breach. Transitions higher on the inner slope might be more critical. A hole in the layer of clay created at a large mean overtopping discharge of 50 l/s per m or more which reaches the under laying sand core, will give a very quick ongoing erosion. Although a test with a parking place of bricks showed that sand erosion at 10 l/s per m or more is very fast (the experiment was even stopped at 30 l/s per m due to fast ongoing damage to the parking area) the dike itself was not in danger at all. Small obstacles like poles and fences did not show any erosion. Small holes from mice and moles did not initiate damage to the grass cover layer. An obstacle like a concrete staircase on the inner slope was totally destroyed at a stage with 75 l/s per m overtopping but the dike itself was not in danger. | Inner slopes of a dike, covered with grass on clay, never failed by overtopping wave erosion for a mean overtopping discharge of 30 l/s per m or less. Only one section failed at 50 l/s per m; some although not all at 75 l/s per m (example Fig. 5). Large erosion resistance of the inner slope of a dike is determined by the combination of grass and clay. The grass cover seems stronger if it grows on sandy clay and may even resist up to 75 l/s per m. But if significant damage occurs, the clay layer is not very erosion resistant. Since grass roots can barely penetrate good quality clay, no strong grass cover could be found. Here grass may rip off for overtopping discharges around 30 l/s per m although the remaining good quality clay layer, still reinforced with some roots, has a large erosion resistance against overtopping waves. Therefore a good grass cover on a sandy clay and a worse grass cover on good clay show different failure mechanisms but similar strength against wave overtopping. Thus the grass sod and its way of maintenance may have less influence on the total strength than previously anticipated. Bad grass coverage (small open areas without grass) on sandy clay may show less resistance. Transitions from slope to horizontal such as the transition from the inner slope to the toe of the dike are probably the most critical locations for initial and increasing damage. Damage here was initiated by a mean discharge of 10 l/s per m or more. As the damage occurred at the lowest part of the inner slope it will take time for damage to extend to the crest level and subsequently cause a dike breach. Transitions higher on the inner slope might be more critical. A hole in the layer of clay created at a large mean overtopping discharge of 50 l/s per m or more which reaches the under laying sand core, will give a very quick ongoing erosion. Although a test with a parking place of bricks showed that sand erosion at 10 l/s per m or more is very fast (the experiment was even stopped at 30 l/s per m due to fast ongoing damage to the parking area) the dike itself was not in danger at all. Small obstacles like poles and fences did not show any erosion. Small holes from mice and moles did not initiate damage to the grass cover layer. An obstacle like a concrete staircase on the inner slope was totally destroyed at a stage with 75 l/s per m overtopping but the dike itself was not in danger. | ||
| − | == | + | ==Modelling of wave overtopping rates== |
| − | + | Modelling of wave overtopping at breakwaters, dikes and seawalls is dealt with in the articles: | |
| − | + | * [[Modelling coastal hydrodynamics]] | |
| + | * [[Hydrodynamic numerical models of wave-structure interaction]] | ||
| − | == | + | ==Eurotop manual== |
| − | + | A review of methods for determining wave overtopping rates at structures in the surf zone is presented in the EurOtop manual 2018 <ref name=OM/>. Empirical formulae are given for various types of structures and examples are shown of damage occurring as a consequence of wave overtopping. | |
| − | == | + | ==Related articles== |
| − | + | * [[Stability of rubble mound breakwaters and shore revetments]] | |
| − | |||
{{THESEUS}} | {{THESEUS}} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 22:13, 18 September 2020
Contents
Introduction
In 1953 the Netherlands experienced a major flooding. Studies determined that most of the dike breaches were caused by overtopping (and even overflowing) of the dikes; failure started at the landward slope of the structures[1]. At that time, all dikes had a rather low crest and were built with a steep landward slope. Since then all major water defences were raised and the landward slopes were made more gentle. The dikes in the western part of the Netherlands were raised such that overtopping rates exceeding 0.1 l/s per meter would have a probability not greater than 1/10,000 per year. In the 1990ties it was decided by law that all major water defences should be periodically assessed for safety (periodicity of about 6 years). In the first safety assessment it was found that a large number of dikes had to be raised again in order to comply with the safety standards. This raised the question if the method to determine the rate of wave overtopping was correct or not. Also the question was put forward if the safety standard of 0.1 l/s per meter with a 1/10,000 probability was adequate. It turned out that the flooding mechanisms were not understood well enough and that the safety standard was wrongfully determined on basis of testing with overflow instead of overtopping. Additionally, failure mechanisms were not adequately described. This lead to a Dutch national research program on loads on and strength of flood defences. To assess the erosion strength of grass covers on inner slopes and transition zones between slope to horizontal flats, destructive tests using a Wave Overtopping Simulator were performed at several dikes in the Netherlands. A Wave Overtopping Simulator (see Fig. 3) performs destructive tests on inner slopes of real dikes in order to establish the erosion resistance against overtopping waves from severe storms.
Definition, design and function
Dikes and levees are applied wherever a hinterland needs protection against flooding. These protection measures prevent an area from flooding thus enabling economic and social activities also at high water levels. The dikes are designed in such a way that they are geotechnically stable under normal and extreme conditions. Dutch dikes are designed to avoid overtopping. Of course no overtopping cannot be guaranteed. The structures which are described here are mainly dikes with grass-covered inner (landward) slopes such as the ones found in the Netherlands. They are mostly made with a sand core covered by a clay layer on the slopes and the crest.
The typical geometry of dikes and levees is an outer or seaward slope then a crest and then a landward slope (right-hand side of Figure 1). The function of the landward slopes is to ensure stability of the dike structure and to guide overtopping waves or water flowing over the crest to the inlands. The landward slopes must be able to resist loads induced by design conditions. The slope angles as well as the width of the crest vary. In the Dutch case, sea dikes have a typical landward slope 1v:3h. River dikes are mostly steeper, up to 1v:2h. The height of the dikes is also highly variable. It depends on the local hydraulic conditions and on the norm frequency of water level for which the dike is designed. This varies from 1/10,000 per year for sea defences in the western part of the Netherlands to 1:1,250 years for dikes along rivers.
Dikes and levees protect up to a certain level. Absolute safety is impossible. The level to which a dike or a levee protects from flooding depends on the hydraulic regime, the physics of the structure (geometric and geotechnical) and the intended risk reduction or allowable risk to which it is designed. This implies that an economic optimum (or in some cases the availability of funds) defines the achievable level of risk reduction. More than half of the Netherlands is below sea level and therefore has to be protected by dikes or other flood protection structures (including dunes). The dikes in the Netherlands are currently designed based on exceedance of a certain water level that is extrapolated from a long time series (over 200 years) and scientific hindcasting. From these water levels, corresponding wave action is calculated. The combination of water level and hydraulic conditions determines the design conditions. Back in 1956, the first Delta Committee already did some early calculations and concluded that the level of protection of the western part of the Netherlands should be higher than in other parts (highest economic value). They found that this part should have a protection level (based on exceedance of water level) of 1/100,000 per year. They knew dikes to have a large residual strength in the designs. They assumed this to be a factor 10 resulting in lowering the norm to once in ten thousand years. In 1996 the safety levels in the Netherlands were registered in the Water Defence Act. In 2009 this Act was replaced by the Water Act. In the Act of 1996 it was stated that the basis for the safety standards should be transformed from exceedance of a certain water level to a risk based approach.
Experimental experience with function and performance
Onset
The landward slope of dikes proved a weak spot during the flooding of 1953 in the Netherlands (over 1,800 people drowned). Back then the dikes were much lower than today. This event led to the Delta Plan recommended heightening the dikes and to reduce the landward slopes to 1:3 or even milder to mitigate the erosive impact of overtopping waves. Before 1953 the landward slopes were very steep, 1:2 or even steeper. Another example is the impact of hurricane Katrina on New Orleans where many landward slopes failed before the water level reached the crest of the levees. Water coming over the dikes or levees does not necessarily mean danger. If the area can cope with a certain amount of water without causing any or just minor socio-economic damage, it may be allowable. To optimize costs and competition for space, the dimensions needed for flood protection is preferably limited. Allowing some water passing the crest of the dike by overtopping waves implies that the need to heighten (and widen) the dikes decreases. If the dikes are strong enough and the amount of overtopping water can be handled, the design level of the structure can be lowered. However, the effect of overtopping water passing the crest of dikes was not well known.
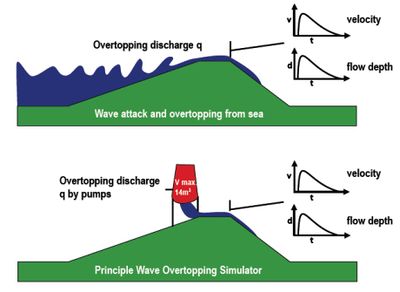
From 2006 and onward, Wave Overtopping Simulators (see Fig. 2) were applied at 19 sections of dikes at 6 different locations in the Netherlands. Destructive tests have shown the behaviour of various inner slopes of dikes, embankments or levees under simulated of wave overtopping, up to a mean overtopping discharge of 125 l/s per m. In the following review is presented, based on four years of destructive testing. Until 2009 overtopping tests with the overtopping simulator have been performed on real Dutch dikes, with hydraulic loads consistent with more or less general extreme sea conditions along the Dutch coast (Hs = 2 m). The tests performed in 2010 were located along a river dike but the hydraulic loads induced were from a sea dike (Hs = 1-3 m). The main reason for this choice was the fact that this dike had a very high sand content (85 and 95%) compared to clay-covered dikes more commonly found along the Dutch sea coast. The core of the dikes is usually sand although in some cases the core of the dike is bolder clay. The cover layer on the landward slopes of sand dikes is typically 0.6 m thick. The thickness of the cover on the sea side is mostly 1 m. In the test locations we indeed found clay covers on the landward slope mainly in the range of 0.6 m but also a location where the thickness of the clay cover only was 0.4 m was found.
Test results

The process of wave overtopping on dikes and levees is fairly well known (Overtopping Manual, 2018[3]). In contrast, the erosive impact of wave overtopping is not well known, mainly due to the fact that research on this topic cannot be performed on a small scale, as it is practically impossible to scale clay and grass down properly. Only some tests have been performed in large wave flumes, like the Delta flume in the Netherlands and the GWK in Germany, see Smith (1994[4]) and Oumeraci et al. (2000[5]). Therefore, the Wave Overtopping Simulator has been developed; see Van der Meer et al. (2006[6], 2007[7] and 2008[2]) for more details. The Simulator consists of a high-level mobile box to store water. The maximum capacity is 5.5 m3 per m width (22 m3 for a 4 m wide Simulator). This box is continuously filled with a predefined discharge and emptied at specific times in such a way that it simulates the overtopping tongue of a wave at the crest and inner slope of a dike, see Fig. 3. The discharge of water is released in such a way that for each overtopping volume of water the flow velocity and thickness of the water tongue at the crest corresponds with the characteristics that can be expected.
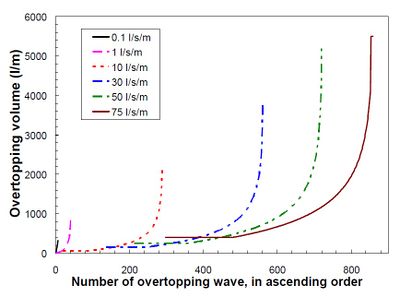
Field tests have been carried out at the end of the winter when grass roots are in their worst condition. The design and calibration of the Wave Overtopping Simulator are described by Van der Meer (2007[7]) and the test results of the first tested dike are described by Akkerman et al. (2007a[8] and 2007b[9]). Part of the tests in 2008 were presented by Steendam et al. (2008[10]). A summary report on all the testing in 2007 and 2008 was written by Van der Meer (2008[2]). Each test condition was given by a mean discharge and lasted for 6 hours. Test conditions increased from 0.1 l/s per m to 1; 5; 10; 30; 50 and 75 l/s per m. A full test on a dike section took about one week and often more than 14,000,000 litres of water flowed over the inner slope of 4 m width. Each test condition consisted of simulation of the required distribution of overtopping volumes (Overtopping Manual, 2007[3]). Such a distribution depends on expected conditions at sea: a larger significant wave height (as at sea dikes) will show fewer overtopping waves, but the volume in the overtopping waves will be bigger than for a smaller wave height (as for example at river dikes). All tests until 2009 have assumed a significant wave height of 2 m with a wave steepness of 0.04 (using the peak period). In 2010 also tests have been performed with a significant wave height of 3 m and 1 m. Distributions of overtopping volumes for this condition and for various mean discharges are given in Figure 4.
Figure 4 clearly shows that for each mean discharge only a relatively small number of waves produce large overtopping volumes (many waves required). The general behaviour of wave overtopping can be described by a large number of fairly small overtopping waves and a few which are much bigger. These few but bigger waves often cause the damage to the inner slope. In the first years of testing it appeared to be very difficult to measure any hydraulic parameter on the inner slope, like flow velocity or flow depth. The maximum flow depth is about 0.25 m. The velocities can approach 8 m/s and the water is very turbulent with a lot of air entrainment (estimated to be about 10%; it was assumed that the front velocity is similar to the maximum depth averaged velocity and that flow velocity and flow depth have the same shape of record in time). Wave overtopping may lead to failure of the crest and inner slope of a dike. In principle there are two different failure mechanisms. Fast overtopping water may damage the surface of the crest and inner slope and, if initial damage or erosion has occurred, this may continue to the layer underneath the grass cover and may lead to an initial breach. This is actually the process which is simulated by the Wave Overtopping Simulator: erosion of the slope. A major failure mechanism on steep inner faces (typically 1:1.5 and 1:2) in the past was slip failure of the (rear) slope. Such slip failures may lead directly to a breach. For this reason most dike designs in the Netherlands in the past fifty years have used a 1:3 inner slope, where it is unlikely that slip failures will occur due to overtopping. This mechanism might however occur for inner slopes steeper than 1:3 and should then be taken into account in safety analysis. This failure mechanism is not simulated by the overtopping tests, as a slip failure needs more width to develop than the 4 m wide test section.

Inner slopes of a dike, covered with grass on clay, never failed by overtopping wave erosion for a mean overtopping discharge of 30 l/s per m or less. Only one section failed at 50 l/s per m; some although not all at 75 l/s per m (example Fig. 5). Large erosion resistance of the inner slope of a dike is determined by the combination of grass and clay. The grass cover seems stronger if it grows on sandy clay and may even resist up to 75 l/s per m. But if significant damage occurs, the clay layer is not very erosion resistant. Since grass roots can barely penetrate good quality clay, no strong grass cover could be found. Here grass may rip off for overtopping discharges around 30 l/s per m although the remaining good quality clay layer, still reinforced with some roots, has a large erosion resistance against overtopping waves. Therefore a good grass cover on a sandy clay and a worse grass cover on good clay show different failure mechanisms but similar strength against wave overtopping. Thus the grass sod and its way of maintenance may have less influence on the total strength than previously anticipated. Bad grass coverage (small open areas without grass) on sandy clay may show less resistance. Transitions from slope to horizontal such as the transition from the inner slope to the toe of the dike are probably the most critical locations for initial and increasing damage. Damage here was initiated by a mean discharge of 10 l/s per m or more. As the damage occurred at the lowest part of the inner slope it will take time for damage to extend to the crest level and subsequently cause a dike breach. Transitions higher on the inner slope might be more critical. A hole in the layer of clay created at a large mean overtopping discharge of 50 l/s per m or more which reaches the under laying sand core, will give a very quick ongoing erosion. Although a test with a parking place of bricks showed that sand erosion at 10 l/s per m or more is very fast (the experiment was even stopped at 30 l/s per m due to fast ongoing damage to the parking area) the dike itself was not in danger at all. Small obstacles like poles and fences did not show any erosion. Small holes from mice and moles did not initiate damage to the grass cover layer. An obstacle like a concrete staircase on the inner slope was totally destroyed at a stage with 75 l/s per m overtopping but the dike itself was not in danger.
Modelling of wave overtopping rates
Modelling of wave overtopping at breakwaters, dikes and seawalls is dealt with in the articles:
Eurotop manual
A review of methods for determining wave overtopping rates at structures in the surf zone is presented in the EurOtop manual 2018 [3]. Empirical formulae are given for various types of structures and examples are shown of damage occurring as a consequence of wave overtopping.
Related articles
References
- ↑ Gerritsen, H. 2005. What happened in 1953? The Big Flood in the Netherlands in retrospect. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 363: 1271–1291
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Van der Meer, J.W., 2008. Erosion strength of inner slopes of dikes against wave overtopping. Preliminary conclusions after two years of testing with the Wave Overtopping Simulator. Summary Report.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Van der Meer, J.W., Allsop, N.W.H., Bruce, T., De Rouck, J., Kortenhaus, A., Pullen, T., Schüttrumpf, H., Troch, P. and Zanuttigh, B. 2018. EurOtop manual
- ↑ Smith, G.M., 1994. Grasdijken. Graserosie, reststerkte en golfoverslag. WL|Delft Hydraulics report H1565 (In Dutch)
- ↑ Oumeraci, H., Schüttrumpf, H., Möller, J., and Kudella, M., 2000. Large scale model tests on wave overtopping with natural sea states. LWI-Bericht Nr. 852.
- ↑ Van der Meer, J.W., Bernardini, P, Akkerman, G.J., and Hoffmans, G.J.C.M., 2007. The wave overtopping simulator in action. ASCE, proc Coastal Structures, Venice, Italy. Van der Meer, J.W., W. Snijders and E. Regeling, 2006. The wave overtopping simulator. ASCE, proc. ICCE 2006, San Diego, 4654-4666.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Van der Meer, J.W., Steendam, G.J., de Raat, G. and Bernardini, P., 2008. Further developments on the wave overtopping simulator. ASCE, proc. ICCE 2008, Hamburg. Van der Meer, J.W., 2007. Design, construction, calibration and use of the wave overtopping simulator. ComCoast, Workpackage 3: Development of Alternative Overtopping-Resistant Sea Defences, phase 3. [www.comcoast.org].
- ↑ Akkerman, G.J., Bernardini, P, van der Meer, J.W., Verheij, H., van Hoven, A., 2007a. Field tests on sea defences subject to wave overtopping. ASCE, proc. Coastal Structures CSt07, Venice, Italy.
- ↑ Akkerman, G.J, van Gerven, K.A.J., Schaap, H.A., and van der Meer, J.W., 2007b. Wave overtopping erosion tests at Groningen sea dyke. ComCoast, Work package 3: Development of Alternative Overtopping-Resistant Sea Defences, phase 3. [www.comcoast.org].
- ↑ Steendam, G.J., de Vries, W., van der Meer, J.W., van Hoven, A., de Raat, G. and Frissel, J.Y. , 2008. Influence of management and maintenance on erosive impact of wave overtopping on grass covered slopes of dikes. Proc. FloodRisk, Oxford, UK.
Please note that others may also have edited the contents of this article.
|