Difference between revisions of "Quinoxyfen"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Definition|title= quinoxyfen | {{Definition|title= quinoxyfen | ||
| − | |definition=Quinoxyfen is the active ingredient in fungicides which are mainly used to control powdery mildew infections on grapes and hops. It cannot control existing or latent infections, therefore, the pesticide must be applied before infections occur. At room temperature it appears as an off white flocculent solid | + | |definition=Quinoxyfen is the active ingredient in fungicides which are mainly used to control powdery mildew infections on grapes and hops. It cannot control existing or latent infections, therefore, the pesticide must be applied before infections occur. At room temperature it appears as an off white flocculent solid<ref name="Ca">[http://www.cdpr.ca.gov/docs/registration/ais/publicreports/5789.pdf CALIFORNIA DEPARTMENT OF PESTICIDE REGULATION 2004 PUBLIC REPORT 2004-01 Quinoxyfen]</ref> <ref name="EU">[http://ec.europa.eu/food/plant/protection/evaluation/newactive/quinoxyfen.pdf EUROPEAN COMMISSION 2003 COMMISSION WORKING DOCUMENT 6781/VI/97-Final Quinoxyfen]</ref>. |
| − | <ref name="Ca">[http://www.cdpr.ca.gov/docs/registration/ais/publicreports/5789.pdf CALIFORNIA DEPARTMENT OF PESTICIDE REGULATION 2004 PUBLIC REPORT 2004-01 Quinoxyfen]</ref> <ref name="EU">[http://ec.europa.eu/food/plant/protection/evaluation/newactive/quinoxyfen.pdf EUROPEAN COMMISSION 2003 COMMISSION WORKING DOCUMENT 6781/VI/97-Final Quinoxyfen]</ref>}} | + | }} |
Revision as of 10:45, 31 August 2009
Definition of quinoxyfen:
Quinoxyfen is the active ingredient in fungicides which are mainly used to control powdery mildew infections on grapes and hops. It cannot control existing or latent infections, therefore, the pesticide must be applied before infections occur. At room temperature it appears as an off white flocculent solid[1] [2].
This is the common definition for quinoxyfen, other definitions can be discussed in the article
|
Notes
| Quinoxyfen |
|---|
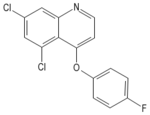
|
| Formula |
| C15H8Cl2FNO |
Quinoxyfen has a low water solubility of 0.047 mg/l and is expected to adsorb to soils and organic matter. Although it is relatively fast degraded in water (halve life of less than 20 days, in soils it can take up to 200 days before it's concentration is halved. Removal of quinoxyfen from the system by degradation can therefore take more than 500 days. From surface water it has a low tendency to evaporate into the atmosphere, where it is rapidly (within a few days) degraded.[2]
It has potential to bioaccumulate in fishes, which can accumulate up to 5000 times the concentration of their environment.[2]
Concentrations above 0,200 mg/l are necessary to cause acute toxicity in fishes, although continued exposure to concentrations above 0.014 mg/l are also expected to be lethal. At concentrations above 0,025 mg/l it can also cause acute toxicity to aquatic invertebrates and algae. Considering that quinoxyfen might biomagnify through food chains there might be risk for secondary poisoning. It might cause toxic effects when mammals consume each day more than 20 mg quinoxyfen per kg of body weight. [2]
Environmental standards and legislation
Included in the water framework list of priority substances