Difference between revisions of "Sea level rise"
Dronkers J (talk | contribs) |
Dronkers J (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
==Contributions to sea-level rise== | ==Contributions to sea-level rise== | ||
| − | Sea levels are highly variable over periods ranging from seconds to decades. Sea-level rise is the rising trend averaged over longer periods, which is observed at many coastal stations since a few centuries. Global warming due to human emissions of greenhouse gases is thought to be responsible for strengthening this trend over the last several decades at least <ref name=C> Church, J.A., P.U. Clark, A. Cazenave, J.M. Gregory, S. Jevrejeva, A. Levermann, M.A. Merrifield, G.A. Milne, R.S. Nerem, P.D. Nunn, A.J. Payne, W.T. Pfeffer, D. Stammer and A.S. Unnikrishnan, 2013. Sea Level Change. In: Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Stocker, T.F., D. Qin, G.-K. Plattner, M. Tignor, S.K. Allen, J. Boschung, A. Nauels, Y. Xia, V. Bex and P.M. Midgley (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA.</ref>. Several phenomena contribute to sea-level rise. At global scale, sea-level rise is mainly due to eustatic sea-level rise: the rise of sea level related to increase of the water mass and water volume of the oceans. Eustatic sea-level rise has two components: (1) water volume increase related to decrease of the density (also referred to as steric component) which is mainly due to increasing temperature and (2) water mass increase, which is mainly due to glacier melting (and to a lesser degree due to decrease of surface water and groundwater storage water on land). Other phenomena can substantially influence sea levels at regional scale, inducing either sea-level rise or sea-level fall <ref name=C></ref>. Most important are: (3) vertical earth crust motions (in particular earth crust adjustment to melting of polar ice caps, the so-called isostatic rebound), (4) land surface subsidence related to soil compaction (in particular due to drainage of peat soils, extraction of groundwater and oil/gas mining), (5) changes in the earth gravitational field related to melting of polar ice caps, (6) changes in the strength and distribution of ocean currents, (7) changes in seawater salinity, (8) regional atmospheric pressure anomalies. Due to these phenomena, sea-level rise is not uniform around the globe, but differs from place to place. [[Relative sea level|Relative sea-level]] rise is the locally observed rise of the average sea level with respect to the land level. It is the sum of the components (1-8). | + | Sea levels are highly variable over periods ranging from seconds to decades. Sea-level rise is the rising trend averaged over longer periods, which is observed at many coastal stations since a few centuries. Global warming due to human emissions of greenhouse gases is thought to be responsible for strengthening this trend over the last several decades at least <ref name=C> Church, J.A., P.U. Clark, A. Cazenave, J.M. Gregory, S. Jevrejeva, A. Levermann, M.A. Merrifield, G.A. Milne, R.S. Nerem, P.D. Nunn, A.J. Payne, W.T. Pfeffer, D. Stammer and A.S. Unnikrishnan, 2013. Sea Level Change. In: Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Stocker, T.F., D. Qin, G.-K. Plattner, M. Tignor, S.K. Allen, J. Boschung, A. Nauels, Y. Xia, V. Bex and P.M. Midgley (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA.</ref>. Several phenomena contribute to sea-level rise. At global scale, sea-level rise is mainly due to eustatic sea-level rise: the rise of sea level related to increase of the water mass and water volume of the oceans. Eustatic sea-level rise has two components: |
| + | |||
| + | (1) water volume increase related to decrease of the density (also referred to as steric component) which is mainly due to increasing temperature and | ||
| + | |||
| + | (2) water mass increase, which is mainly due to glacier melting (and to a lesser degree due to decrease of surface water and groundwater storage water on land). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Other phenomena can substantially influence sea levels at regional scale, inducing either sea-level rise or sea-level fall <ref name=C></ref>. Most important are: | ||
| + | |||
| + | (3) vertical earth crust motions (in particular earth crust adjustment to melting of polar ice caps, the so-called isostatic rebound), | ||
| + | |||
| + | (4) land surface subsidence related to soil compaction (in particular due to drainage of peat soils, extraction of groundwater and oil/gas mining), | ||
| + | |||
| + | (5) changes in the earth gravitational field related to melting of polar ice caps, (6) changes in the strength and distribution of ocean currents, | ||
| + | |||
| + | (7) changes in seawater salinity, and | ||
| + | |||
| + | (8) regional atmospheric pressure anomalies. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Due to these phenomena, sea-level rise is not uniform around the globe, but differs from place to place. [[Relative sea level|Relative sea-level]] rise is the locally observed rise of the average sea level with respect to the land level. It is the sum of the components (1-8). | ||
| Line 15: | Line 33: | ||
Trend analyses of regularly updated satellite data can be viewed at the NOAA site <ref> https://www.star.nesdis.noaa.gov/sod/lsa/SeaLevelRise/LSA_SLR_timeseries.php </ref> for global and regional sea level changes around the world. | Trend analyses of regularly updated satellite data can be viewed at the NOAA site <ref> https://www.star.nesdis.noaa.gov/sod/lsa/SeaLevelRise/LSA_SLR_timeseries.php </ref> for global and regional sea level changes around the world. | ||
| − | Even after correcting for the effect of glacial isostatic adjustment substantial regional differences in sea-level rise occur<ref> Slangen A.B.A., Katsman C.A., van der Wal R.S.W., Vermeersen L.L.A. and Riva R.E.M. 2012. Towards regional projections of twenty-first century sea-level change using IPCC SRES scenarios. Clim. Dyn. 38 (5): 1191-1209, doi:10.1007/s00382-011-1057-6.</ref>. Major causes are: | + | Even after correcting for the effect of glacial isostatic adjustment substantial regional differences in sea-level rise occur <ref> Slangen A.B.A., Katsman C.A., van der Wal R.S.W., Vermeersen L.L.A. and Riva R.E.M. 2012. Towards regional projections of twenty-first century sea-level change using IPCC SRES scenarios. Clim. Dyn. 38 (5): 1191-1209, doi:10.1007/s00382-011-1057-6.</ref>. Major causes are: |
* elastic solid Earth deformation and self-gravitation related to changes in land ice; | * elastic solid Earth deformation and self-gravitation related to changes in land ice; | ||
* changes in seawater density related to the influence of fresh water input, ocean currents and atmospheric temperature. | * changes in seawater density related to the influence of fresh water input, ocean currents and atmospheric temperature. | ||
| Line 41: | Line 59: | ||
Sea-level rise will impact in particular on low-lying coastal regions, such as river deltas and coral islands<ref> Overeem, I. and Syvitski, J.P.M. 2009. Dynamics and Vulnerability of Delta Systems. LOICZ Reports & Studies No. 35. GKSS Research Center, Geesthacht, 54 pages.</ref>. These coastal zones are shaped under the influence of marine bio-geomorphological processes which limit their elevation to the level of high-water. Many of these regions are densely populated and host very large cities, especially in developing countries. In these regions, sea-level rise is generally exacerbated by soil compaction and land subsidence in connection with drainage works and the extraction of groundwater or oil / gas mining. The vulnerability of many of these deltas is further enhanced by coastal erosion, because of sediment retention behind upstream dams, hard coastal structures and/or conversion of mangrove forests to aquacultures <ref> Syvitski, J.P., Kettner, A.J., Overeem, L., Hutton, E.W., Hannon, M.T., Brakenridge, G.R., Day, J., Vörösmarty, C., Saito, Y. and Giosan, L. 2009. Sinking deltas due to human activities. Nature Geosci. 2: 681–686.</ref><ref> Hanson, S., Nicholls, R., Ranger, N., Hallegatte, S., Corfee-Morlot, J., Herweijer, C. and Chateau, J. 2011. A global ranking of port cities with high exposure to climate extremes. Climatic Change 104: 89–111. DOI 10.1007/s10584-010-9977-4</ref>, see [[Human causes of coastal erosion]]. Considerable investments are required for adaptation to sea-level rise in these vulnerable coastal regions, in particular to reduce flooding risks <ref> Hinkel, J., D.P. van Vuuren, R.J. Nicholls, and Klein, R.J.T. 2013. The effects of mitigation and adaptation on coastal impacts in the 21st century. An application of the DIVA and IMAGE models. Climatic Change 117(4): 783-794.</ref>. | Sea-level rise will impact in particular on low-lying coastal regions, such as river deltas and coral islands<ref> Overeem, I. and Syvitski, J.P.M. 2009. Dynamics and Vulnerability of Delta Systems. LOICZ Reports & Studies No. 35. GKSS Research Center, Geesthacht, 54 pages.</ref>. These coastal zones are shaped under the influence of marine bio-geomorphological processes which limit their elevation to the level of high-water. Many of these regions are densely populated and host very large cities, especially in developing countries. In these regions, sea-level rise is generally exacerbated by soil compaction and land subsidence in connection with drainage works and the extraction of groundwater or oil / gas mining. The vulnerability of many of these deltas is further enhanced by coastal erosion, because of sediment retention behind upstream dams, hard coastal structures and/or conversion of mangrove forests to aquacultures <ref> Syvitski, J.P., Kettner, A.J., Overeem, L., Hutton, E.W., Hannon, M.T., Brakenridge, G.R., Day, J., Vörösmarty, C., Saito, Y. and Giosan, L. 2009. Sinking deltas due to human activities. Nature Geosci. 2: 681–686.</ref><ref> Hanson, S., Nicholls, R., Ranger, N., Hallegatte, S., Corfee-Morlot, J., Herweijer, C. and Chateau, J. 2011. A global ranking of port cities with high exposure to climate extremes. Climatic Change 104: 89–111. DOI 10.1007/s10584-010-9977-4</ref>, see [[Human causes of coastal erosion]]. Considerable investments are required for adaptation to sea-level rise in these vulnerable coastal regions, in particular to reduce flooding risks <ref> Hinkel, J., D.P. van Vuuren, R.J. Nicholls, and Klein, R.J.T. 2013. The effects of mitigation and adaptation on coastal impacts in the 21st century. An application of the DIVA and IMAGE models. Climatic Change 117(4): 783-794.</ref>. | ||
| − | Sea-level rise enhances shoreline retreat (for retreating coasts) or reduce shoreline progradation (for accreting coasts), see [[Natural causes of coastal erosion]]. The influence of sea-level rise on the shoreline position can be estimated by means of the [[Bruun rule]] <ref> Atkinson, A.L., Baldock, T.E., Birrien, F., Callaghan, D.P., Nielsen, P., Beuzen, T., Turner, I.I., Blenkinsopp, C.E. and Ranasinghe, R. 2018. Laboratory investigation of the Bruun Rule and beach response to sea level rise. Coastal Engineering 136: 183–202.</ref>. | + | Sea-level rise enhances shoreline retreat (for retreating coasts) or reduce shoreline progradation (for accreting coasts), see [[Natural causes of coastal erosion]]. The influence of sea-level rise on the shoreline position can be estimated by means of the [[Parametric equilibrium models| Bruun rule]] <ref> Atkinson, A.L., Baldock, T.E., Birrien, F., Callaghan, D.P., Nielsen, P., Beuzen, T., Turner, I.I., Blenkinsopp, C.E. and Ranasinghe, R. 2018. Laboratory investigation of the Bruun Rule and beach response to sea level rise. Coastal Engineering 136: 183–202.</ref>. |
| − | Strategies for dealing with the impacts of sea-level rise depend on local conditions. Different strategies are reviewed in the 5th IPCC Assessment report<ref name=W></ref> <ref> Noble, I.R., S. Huq, Y.A. Anokhin, J. Carmin, D. Goudou, F.P. Lansigan, B. Osman-Elasha, and A. Villamizar, 2014. Adaptation needs and options. In: Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Part A: Global and Sectoral Aspects. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Field, C.B., V.R. Barros, D.J. Dokken, K.J. Mach, M.D. Mastrandrea, T.E. Bilir, M. Chatterjee, K.L. Ebi, Y.O. Estrada, R.C. Genova, B. Girma, E.S. Kissel, A.N. Levy, S. MacCracken, P.R. Mastrandrea, and L.L. White (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 833-868.</ref> | + | Strategies for dealing with the impacts of sea-level rise depend on local conditions. Different strategies are reviewed in the 5th IPCC Assessment report<ref name=W></ref> <ref> Noble, I.R., S. Huq, Y.A. Anokhin, J. Carmin, D. Goudou, F.P. Lansigan, B. Osman-Elasha, and A. Villamizar, 2014. Adaptation needs and options. In: Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Part A: Global and Sectoral Aspects. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Field, C.B., V.R. Barros, D.J. Dokken, K.J. Mach, M.D. Mastrandrea, T.E. Bilir, M. Chatterjee, K.L. Ebi, Y.O. Estrada, R.C. Genova, B. Girma, E.S. Kissel, A.N. Levy, S. MacCracken, P.R. Mastrandrea, and L.L. White (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 833-868.</ref>. |
| Line 50: | Line 68: | ||
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sea_level_rise | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sea_level_rise | ||
| − | + | [[Potential Impacts of Sea Level Rise on Mangroves]] | |
| − | |||
| − | [[ | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| Line 73: | Line 87: | ||
[[Category:Land and ocean interactions]] | [[Category:Land and ocean interactions]] | ||
[[Category:Geomorphological processes and natural coastal features]] | [[Category:Geomorphological processes and natural coastal features]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Relative sea level | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{Review | ||
| + | |name=Job Dronkers | ||
| + | |AuthorID=120 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{Definition|title=Relative sea level | ||
| + | |definition= The relative sea level is the mean sea level related to a local reference land level.}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Relative sea level change== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The relative sea level changes as a consequence of [[Sea level rise]]. It changes also due to vertical motions of the land level. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Global warming is a major cause of sea-level rise. The global mean sea level rises as a consequence of: | ||
| + | * Increase of the ocean water mass, due to melting of land ice (in particular the polar ice caps) and due to decrease of groundwater and surface water storage on land; | ||
| + | * Expansion of the ocean water volume due to decrease of water density with increasing temperature. | ||
| + | The influence of global warming on sea-level rise varies along the world's coastlines as a consequence of <ref> Slangen A.B.A., Katsman C.A., van der Wal R.S.W., Vermeersen L.L.A. and Riva R.E.M. 2012. Towards regional projections of twenty-first century sea-level change using IPCC SRES scenarios. Clim. Dyn. 38 (5): 1191-1209, doi:10.1007/s00382-011-1057-6.</ref>: | ||
| + | * Residual changes in the strength and distribution of ocean currents; | ||
| + | * Residual changes in atmospheric pressure distribution; | ||
| + | * Residual local changes in seawater salinity; | ||
| + | * Changes in the earth gravitational field related to melting of polar ice caps. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Land level change occurs as a consequence of: | ||
| + | * Isostatic rebound: adjustment of the earth crust due to melting of polar ice caps, causing a rise of the formerly covered areas and a sink of adjacent areas that were not covered; | ||
| + | * Tectonic activity; | ||
| + | * Land subsidence due to soil compaction caused by groundwater extraction, oil/gas mining and/or drainage of organic soils. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Relative sea level change is the net result of these different factors. This implies in most cases a relative rise of the mean sea level, which in some regions may even be substantially stronger than the rise of the global mean sea level. However, in some other regions with strong land uplift the relative sea level is still falling. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Response of the coastal system to sea level changes== | ||
| + | The response of the coast to sea level changes can be classified as: | ||
| + | * [[regressive coast]], seaward coastline shift in the case of a falling relative sea level; | ||
| + | * [[transgressive coast]], landward shoreline shift in the case of a rising relative sea level; | ||
| + | * [[prograding coast]], seaward coastline shift when net sediment supply to the coast dominates the impact of relative sea-level rise; | ||
| + | * [[retrograding coast]], landward shoreline shift when net sediment supply to the coast is insufficient to compensate for relative sea-level rise. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==See Also== | ||
| + | * [[Sea level rise]] | ||
| + | * [[Potential Impacts of Sea Level Rise on Mangroves]] | ||
| + | * [[Greek case studies: The implications of the expected sea level rise on the low lying areas of continental Greece in the next century]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{author | ||
| + | |AuthorID= 16611 | ||
| + | |AuthorName= AnnaKroon | ||
| + | |AuthorFullName= Anna Kroon}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Climate change]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Coastal flooding management]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Coastal risk management]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Land and ocean interactions]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Geomorphological processes and natural coastal features]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Protection of coastal and marine zones]] | ||
Revision as of 21:51, 9 November 2018
Definition of Sea Level Rise:
The term sea-level rise generally designates the average long-term global rise of the ocean surface measured from the centre of the earth (or more precisely, from the earth reference ellipsoid), as derived from satellite observations. Relative sea-level rise refers to long-term average sea-level rise relative to the local land level, as derived from coastal tide gauges.
This is the common definition for Sea Level Rise, other definitions can be discussed in the article
|
Contents
Contributions to sea-level rise
Sea levels are highly variable over periods ranging from seconds to decades. Sea-level rise is the rising trend averaged over longer periods, which is observed at many coastal stations since a few centuries. Global warming due to human emissions of greenhouse gases is thought to be responsible for strengthening this trend over the last several decades at least [1]. Several phenomena contribute to sea-level rise. At global scale, sea-level rise is mainly due to eustatic sea-level rise: the rise of sea level related to increase of the water mass and water volume of the oceans. Eustatic sea-level rise has two components:
(1) water volume increase related to decrease of the density (also referred to as steric component) which is mainly due to increasing temperature and
(2) water mass increase, which is mainly due to glacier melting (and to a lesser degree due to decrease of surface water and groundwater storage water on land).
Other phenomena can substantially influence sea levels at regional scale, inducing either sea-level rise or sea-level fall [1]. Most important are:
(3) vertical earth crust motions (in particular earth crust adjustment to melting of polar ice caps, the so-called isostatic rebound),
(4) land surface subsidence related to soil compaction (in particular due to drainage of peat soils, extraction of groundwater and oil/gas mining),
(5) changes in the earth gravitational field related to melting of polar ice caps, (6) changes in the strength and distribution of ocean currents,
(7) changes in seawater salinity, and
(8) regional atmospheric pressure anomalies.
Due to these phenomena, sea-level rise is not uniform around the globe, but differs from place to place. Relative sea-level rise is the locally observed rise of the average sea level with respect to the land level. It is the sum of the components (1-8).
Observed sea-level rise
Trends in sea-level from world-wide available tide gauge records and from satellite measurements have been analysed by Church and White [2]. The tide gauge data were corrected for vertical land surface motion, by using estimates for glacial isostatic adjustment (assuming that this is the major cause of vertical land surface motion). From these corrected tide gauge data, a linear trend of 1.7 ± 0.2 mm/year sea-level rise was found for the period 1900 to 1990 and a linear trend of 2.8 ± 0.8 mm/year for the period 1990 to 2009. From the satellite data a linear trend of 3.2 ± 0.4 mm/year was derived for the the same perod 1990 to 2009. From this analysis the authors conclude that there is a significant strengthening of sea-level rise during the last decades.
Trend analyses of regularly updated satellite data can be viewed at the NOAA site [3] for global and regional sea level changes around the world.
Even after correcting for the effect of glacial isostatic adjustment substantial regional differences in sea-level rise occur [4]. Major causes are:
- elastic solid Earth deformation and self-gravitation related to changes in land ice;
- changes in seawater density related to the influence of fresh water input, ocean currents and atmospheric temperature.
Projections of future sea-level rise
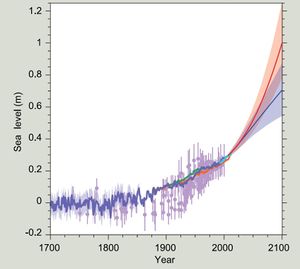
Many model studies have been carried out for predicting future sea-level rise [5]. A large spread of future forecasted levels results from uncertainties in future emissions of greenhouse gases, from shortcomings in the present understanding of climate dynamics (including ocean-atmosphere interaction) and from restrictions imposed on model grid scales. Figure 1 shows a compilation of model forecasts up till 2100 presented in the 5th IPCC Assessment Report[1]. The models predict an increase of the rate of sea-level rise. Recent insight in the response of ice cap melting to global warming, which is not yet included in these projections, points to an even stronger increase [6].
Sea-level rise lags behind global warming. Even if greenhouse gas emissions would stop today, sea levels will continue rising for at least a century [7].
Impact of sea-level rise
Sea-level rise will impact in particular on low-lying coastal regions, such as river deltas and coral islands[8]. These coastal zones are shaped under the influence of marine bio-geomorphological processes which limit their elevation to the level of high-water. Many of these regions are densely populated and host very large cities, especially in developing countries. In these regions, sea-level rise is generally exacerbated by soil compaction and land subsidence in connection with drainage works and the extraction of groundwater or oil / gas mining. The vulnerability of many of these deltas is further enhanced by coastal erosion, because of sediment retention behind upstream dams, hard coastal structures and/or conversion of mangrove forests to aquacultures [9][10], see Human causes of coastal erosion. Considerable investments are required for adaptation to sea-level rise in these vulnerable coastal regions, in particular to reduce flooding risks [11]. Sea-level rise enhances shoreline retreat (for retreating coasts) or reduce shoreline progradation (for accreting coasts), see Natural causes of coastal erosion. The influence of sea-level rise on the shoreline position can be estimated by means of the Bruun rule [12].
Strategies for dealing with the impacts of sea-level rise depend on local conditions. Different strategies are reviewed in the 5th IPCC Assessment report[5] [13].
See also
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sea_level_rise
Potential Impacts of Sea Level Rise on Mangroves
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Church, J.A., P.U. Clark, A. Cazenave, J.M. Gregory, S. Jevrejeva, A. Levermann, M.A. Merrifield, G.A. Milne, R.S. Nerem, P.D. Nunn, A.J. Payne, W.T. Pfeffer, D. Stammer and A.S. Unnikrishnan, 2013. Sea Level Change. In: Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Stocker, T.F., D. Qin, G.-K. Plattner, M. Tignor, S.K. Allen, J. Boschung, A. Nauels, Y. Xia, V. Bex and P.M. Midgley (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA.
- ↑ Church J.A. and White N.J. 2011. Sea-Level Rise from the Late 19th to the Early 21st Century. Surv.Geophys 32: 585–602, DOI 10.1007/s10712-011-9119-1
- ↑ https://www.star.nesdis.noaa.gov/sod/lsa/SeaLevelRise/LSA_SLR_timeseries.php
- ↑ Slangen A.B.A., Katsman C.A., van der Wal R.S.W., Vermeersen L.L.A. and Riva R.E.M. 2012. Towards regional projections of twenty-first century sea-level change using IPCC SRES scenarios. Clim. Dyn. 38 (5): 1191-1209, doi:10.1007/s00382-011-1057-6.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Wong , P.P., I.J. Losada, J.-P. Gattuso, J. Hinkel, A. Khattabi, K.L. McInnes, Y. Saito, and A. Sallenger, 2014. Coastal systems and low-lying areas. In: Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Part A: Global and Sectoral Aspects. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Field, C.B., V.R. Barros, D.J. Dokken, K.J. Mach, M.D. Mastrandrea, T.E. Bilir, M. Chatterjee, K.L. Ebi, Y.O. Estrada, R.C. Genova, B. Girma, E.S. Kissel, A.N. Levy, S. MacCracken, P.R. Mastrandrea, and L.L. White (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 361-409.
- ↑ Hansen, J., Sato, M., Hearty, P., Ruedy, R., Kelley, M., Masson-Delmotte, V., Russell, G., Tselioudis, G., Cao, J., Rignot, E., Velicogna, I., Kandiano, E., von Schuckmann, K., Kharecha, P., Legrande, A.N., Bauer, M. and Lo, K.-W. 2015. Ice melt, sea level rise and superstorms: evidence from paleoclimate data, climate modeling, and modern observations that 2◦ C global warming is highly dangerous. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Discussions 15: 20059–20179.
- ↑ Mengel, M., Nauels, A., Rogelj, J. and Schleussner, C.-F. 2018. Committed sea-level rise under the Paris Agreement and the legacy of delayed mitigation action. Nature Communications 9, Article number 601.
- ↑ Overeem, I. and Syvitski, J.P.M. 2009. Dynamics and Vulnerability of Delta Systems. LOICZ Reports & Studies No. 35. GKSS Research Center, Geesthacht, 54 pages.
- ↑ Syvitski, J.P., Kettner, A.J., Overeem, L., Hutton, E.W., Hannon, M.T., Brakenridge, G.R., Day, J., Vörösmarty, C., Saito, Y. and Giosan, L. 2009. Sinking deltas due to human activities. Nature Geosci. 2: 681–686.
- ↑ Hanson, S., Nicholls, R., Ranger, N., Hallegatte, S., Corfee-Morlot, J., Herweijer, C. and Chateau, J. 2011. A global ranking of port cities with high exposure to climate extremes. Climatic Change 104: 89–111. DOI 10.1007/s10584-010-9977-4
- ↑ Hinkel, J., D.P. van Vuuren, R.J. Nicholls, and Klein, R.J.T. 2013. The effects of mitigation and adaptation on coastal impacts in the 21st century. An application of the DIVA and IMAGE models. Climatic Change 117(4): 783-794.
- ↑ Atkinson, A.L., Baldock, T.E., Birrien, F., Callaghan, D.P., Nielsen, P., Beuzen, T., Turner, I.I., Blenkinsopp, C.E. and Ranasinghe, R. 2018. Laboratory investigation of the Bruun Rule and beach response to sea level rise. Coastal Engineering 136: 183–202.
- ↑ Noble, I.R., S. Huq, Y.A. Anokhin, J. Carmin, D. Goudou, F.P. Lansigan, B. Osman-Elasha, and A. Villamizar, 2014. Adaptation needs and options. In: Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Part A: Global and Sectoral Aspects. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Field, C.B., V.R. Barros, D.J. Dokken, K.J. Mach, M.D. Mastrandrea, T.E. Bilir, M. Chatterjee, K.L. Ebi, Y.O. Estrada, R.C. Genova, B. Girma, E.S. Kissel, A.N. Levy, S. MacCracken, P.R. Mastrandrea, and L.L. White (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 833-868.
Please note that others may also have edited the contents of this article.
|
Relative sea level
Definition of Relative sea level:
The relative sea level is the mean sea level related to a local reference land level.
This is the common definition for Relative sea level, other definitions can be discussed in the article
|
Relative sea level change
The relative sea level changes as a consequence of Sea level rise. It changes also due to vertical motions of the land level.
Global warming is a major cause of sea-level rise. The global mean sea level rises as a consequence of:
- Increase of the ocean water mass, due to melting of land ice (in particular the polar ice caps) and due to decrease of groundwater and surface water storage on land;
- Expansion of the ocean water volume due to decrease of water density with increasing temperature.
The influence of global warming on sea-level rise varies along the world's coastlines as a consequence of [1]:
- Residual changes in the strength and distribution of ocean currents;
- Residual changes in atmospheric pressure distribution;
- Residual local changes in seawater salinity;
- Changes in the earth gravitational field related to melting of polar ice caps.
Land level change occurs as a consequence of:
- Isostatic rebound: adjustment of the earth crust due to melting of polar ice caps, causing a rise of the formerly covered areas and a sink of adjacent areas that were not covered;
- Tectonic activity;
- Land subsidence due to soil compaction caused by groundwater extraction, oil/gas mining and/or drainage of organic soils.
Relative sea level change is the net result of these different factors. This implies in most cases a relative rise of the mean sea level, which in some regions may even be substantially stronger than the rise of the global mean sea level. However, in some other regions with strong land uplift the relative sea level is still falling.
Response of the coastal system to sea level changes
The response of the coast to sea level changes can be classified as:
- regressive coast, seaward coastline shift in the case of a falling relative sea level;
- transgressive coast, landward shoreline shift in the case of a rising relative sea level;
- prograding coast, seaward coastline shift when net sediment supply to the coast dominates the impact of relative sea-level rise;
- retrograding coast, landward shoreline shift when net sediment supply to the coast is insufficient to compensate for relative sea-level rise.
See Also
- Sea level rise
- Potential Impacts of Sea Level Rise on Mangroves
- Greek case studies: The implications of the expected sea level rise on the low lying areas of continental Greece in the next century
References
- ↑ Slangen A.B.A., Katsman C.A., van der Wal R.S.W., Vermeersen L.L.A. and Riva R.E.M. 2012. Towards regional projections of twenty-first century sea-level change using IPCC SRES scenarios. Clim. Dyn. 38 (5): 1191-1209, doi:10.1007/s00382-011-1057-6.
Please note that others may also have edited the contents of this article.
|